
In the digital age, where technology permeates every aspect of our lives, the threat of cyberattacks looms large. One of the most formidable challenges to computer security is the existence of zero-day vulnerabilities, software flaws that are unknown to developers and for which no patches or defenses exist. These vulnerabilities, often exploited by malicious actors, can have devastating consequences, ranging from data breaches to system failures and financial losses.
The impact of zero-day vulnerabilities extends far beyond individual computers. They pose a significant threat to critical infrastructure, including power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks. Moreover, these vulnerabilities can compromise sensitive data in industries such as healthcare, finance, and government, putting sensitive information at risk.
Understanding Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
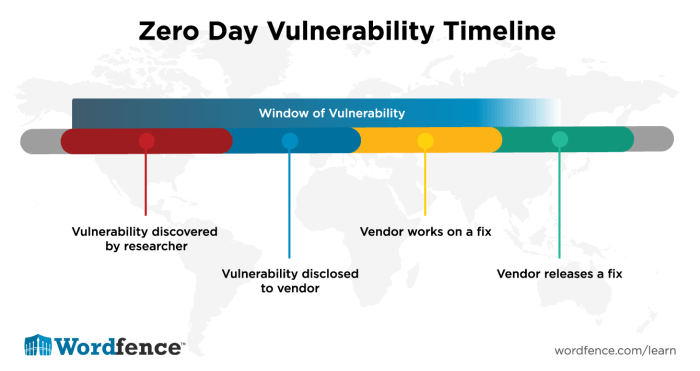
Zero-day vulnerabilities, often referred to as “0-days,” are security flaws in software or hardware that are unknown to the vendor or developer. These vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they are exploited before the vendor has a chance to develop and release a patch or update. Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a significant threat to computer security due to their exploitable nature before any mitigation measures are in place.
They can be used by attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems, steal sensitive data, launch denial-of-service attacks, or install malware.
Characteristics of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities are characterized by their unknown nature, lack of patches or defenses, and potential for significant damage.
- Unknown Nature: The vulnerability is unknown to the vendor, meaning there is no patch or update available to address it. This lack of awareness makes it difficult for security professionals to detect and protect against the vulnerability.
- Lack of Patches or Defenses: Since the vulnerability is unknown, there are no existing patches or defenses to prevent exploitation. This leaves systems vulnerable to attack until a patch is developed and deployed.
- Potential for Significant Damage: Zero-day vulnerabilities can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt critical services, or launch devastating attacks.
Examples of Notable Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Numerous high-profile zero-day vulnerabilities have been discovered and exploited over the years, demonstrating their significant impact across various industries and individuals.
- Stuxnet: This sophisticated malware, discovered in 2010, targeted industrial control systems, specifically those used in Iran’s nuclear program. It exploited vulnerabilities in Siemens software, causing significant damage to centrifuges used for uranium enrichment.
- Heartbleed: In 2014, the Heartbleed vulnerability affected OpenSSL, a widely used cryptographic library. This flaw allowed attackers to steal sensitive information, such as passwords and private keys, from websites and applications that used OpenSSL. The impact was widespread, affecting millions of websites and applications.
- WannaCry: This ransomware attack, which hit computers worldwide in 2017, exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft’s SMB protocol. The attack encrypted files on affected computers, demanding payment in Bitcoin for their decryption. The attack caused widespread disruption to businesses and individuals.
The Impact of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities on Computer Security
Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a significant threat to computer security, as they exploit weaknesses in software, hardware, or network configurations before developers can patch them. These vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they are unknown to security researchers and developers, leaving systems vulnerable to exploitation.
Exploiting Weaknesses in Software, Hardware, or Network Configurations
Zero-day vulnerabilities exploit weaknesses in software, hardware, or network configurations, enabling attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems and data. These vulnerabilities often arise from coding errors, design flaws, or misconfigurations. Attackers can leverage these vulnerabilities to bypass security measures, execute malicious code, and gain control over affected systems. For example, a zero-day vulnerability in a web browser could allow an attacker to inject malicious code into a website, enabling them to steal sensitive information like passwords or credit card details.
Consequences of Successful Zero-Day Attacks
Successful zero-day attacks can have severe consequences, including:
- Data Breaches: Attackers can exploit zero-day vulnerabilities to steal sensitive data, such as customer information, financial records, or intellectual property. This can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- System Failures: Zero-day attacks can cause system failures, leading to disruptions in business operations, downtime, and loss of productivity. For example, a zero-day vulnerability in a critical infrastructure system could cause a power outage or disrupt communication networks.
- Financial Losses: Zero-day attacks can result in significant financial losses due to data breaches, system downtime, and the costs associated with remediation and recovery. Companies may face fines and legal penalties for data breaches, while individuals may suffer financial losses due to identity theft or fraud.
Impact on Different Aspects of Computer Security
Zero-day vulnerabilities can impact different aspects of computer security, including:
- Data Confidentiality: Zero-day attacks can compromise data confidentiality by allowing attackers to access sensitive information. This can lead to data breaches and unauthorized disclosure of confidential data.
- Data Integrity: Zero-day vulnerabilities can compromise data integrity by allowing attackers to modify or delete data without authorization. This can lead to data corruption and loss of data accuracy.
- Data Availability: Zero-day attacks can compromise data availability by causing system failures or denial-of-service attacks. This can disrupt business operations, prevent users from accessing critical systems, and cause significant downtime.
Mitigating the Risks of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
While zero-day vulnerabilities pose a significant threat, there are proactive measures that can be implemented to minimize their impact. These measures focus on strengthening defenses, staying informed about emerging threats, and empowering users to be more vigilant.
Regular Software Updates
Software updates are crucial for patching known vulnerabilities and mitigating the risk of zero-day attacks. They often include fixes for security flaws that could be exploited by attackers.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates on all devices and software. This ensures that security patches are applied as soon as they become available, minimizing the window of vulnerability.
- Prioritize Critical Updates: Focus on installing critical security updates first, as they often address the most severe vulnerabilities.
- Regular Patching Schedule: Establish a regular patching schedule to ensure that systems are consistently updated.
Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify weaknesses in systems and applications. They provide valuable insights into potential vulnerabilities, including zero-day threats.
- Internal Audits: Conduct internal security audits to identify vulnerabilities within your organization’s network and systems.
- External Penetration Testing: Engage external security experts to conduct penetration testing, simulating real-world attacks to uncover vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools: Utilize automated vulnerability scanning tools to identify known vulnerabilities and potential zero-day risks.
Security Software
Security software, including firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems, plays a vital role in mitigating zero-day threats. These tools provide a layer of defense against malicious attacks, including those exploiting unknown vulnerabilities.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access and potentially malicious traffic.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software detects and removes known malware, including threats that exploit zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDSs monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential attacks, including those exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities.
User Education and Awareness
User education and awareness are essential for preventing zero-day attacks. Educated users are less likely to fall victim to phishing scams or click on malicious links, which are common vectors for zero-day exploits.
- Security Training: Provide regular security awareness training to employees and users, covering topics such as phishing, social engineering, and safe browsing practices.
- Phishing Awareness Campaigns: Run phishing awareness campaigns to educate users about the signs of phishing emails and how to avoid them.
- Strong Password Practices: Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable multi-factor authentication where possible.
The Role of Technology in Combating Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
The emergence of zero-day vulnerabilities poses a significant challenge to computer security. These vulnerabilities are unknown to developers and security researchers, making them particularly difficult to defend against. However, technological advancements offer promising solutions for identifying, mitigating, and ultimately preventing the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Zero-Day Vulnerability Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing an increasingly vital role in identifying and mitigating zero-day vulnerabilities. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, including code repositories, network traffic, and system logs, to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate the presence of previously unknown vulnerabilities. These algorithms can learn from past attacks and identify emerging threats based on their characteristics.
AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data, including code repositories, network traffic, and system logs, to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate the presence of previously unknown vulnerabilities.
- Predictive Analysis: AI algorithms can predict potential vulnerabilities based on code patterns and historical attack data. By analyzing the codebase of software, AI can identify potential weaknesses and predict which parts of the code are most likely to be exploited.
- Threat Intelligence: AI and ML can analyze threat intelligence feeds to identify emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This data can be used to train AI models to detect and respond to attacks before they can cause significant damage.
- Vulnerability Assessment: AI-powered vulnerability assessment tools can scan systems for known and unknown vulnerabilities, including zero-day vulnerabilities. These tools can analyze code, network traffic, and system configurations to identify potential weaknesses.
Sandboxing and Virtualization for Threat Isolation and Analysis
Sandboxing and virtualization techniques are essential for isolating and analyzing potential threats, including those stemming from zero-day vulnerabilities. Sandboxing creates a controlled environment where suspicious software or files can be executed without affecting the host system. This allows security researchers to analyze the behavior of malicious code and identify potential vulnerabilities without risking the compromise of the host system.
Sandboxing creates a controlled environment where suspicious software or files can be executed without affecting the host system. This allows security researchers to analyze the behavior of malicious code and identify potential vulnerabilities without risking the compromise of the host system.
- Threat Analysis: Sandboxing enables security researchers to analyze the behavior of malware and other malicious code in a safe environment. This analysis can help identify the vulnerabilities exploited by the malware and develop mitigation strategies.
- Zero-Day Vulnerability Detection: Sandboxing can be used to detect zero-day vulnerabilities by executing suspicious code in a controlled environment and monitoring its behavior. If the code exploits a previously unknown vulnerability, it will be detected within the sandbox, preventing any damage to the host system.
- Vulnerability Research: Virtualization allows security researchers to create and test different system configurations and environments. This can be used to identify vulnerabilities in software and hardware, including zero-day vulnerabilities.
Security Research and Vulnerability Disclosure Programs
Security research and vulnerability disclosure programs play a crucial role in addressing zero-day vulnerabilities. Security researchers are constantly searching for vulnerabilities in software and hardware, and they often share their findings with developers and vendors through responsible disclosure programs. This allows developers to patch vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
Security researchers are constantly searching for vulnerabilities in software and hardware, and they often share their findings with developers and vendors through responsible disclosure programs. This allows developers to patch vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Bug bounty programs incentivize security researchers to find and report vulnerabilities. These programs offer financial rewards for identifying and reporting vulnerabilities, encouraging researchers to focus on finding and disclosing zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Disclosure Policies: Many software vendors have established vulnerability disclosure policies that Artikel the process for reporting vulnerabilities and the timelines for patching them. These policies provide a framework for responsible disclosure and help ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly.
- Security Research Communities: Online security research communities provide a platform for researchers to share information, collaborate on vulnerability research, and develop new security tools. These communities play a vital role in accelerating the discovery and mitigation of zero-day vulnerabilities.
The Impact of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities on Different Technology Sectors

Zero-day vulnerabilities pose significant threats to various technology sectors, with the potential to disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and cause financial losses. The impact of these vulnerabilities varies depending on the sector’s criticality, reliance on technology, and the nature of the attack.
Impact on Healthcare
Zero-day vulnerabilities in healthcare pose a significant risk to patient safety and data privacy. Healthcare organizations rely heavily on technology for patient records, medical devices, and communication systems. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to:
- Data breaches exposing sensitive patient information, including medical records, insurance details, and financial data.
- Disruption of critical medical equipment, such as imaging scanners, ventilators, and infusion pumps, potentially leading to treatment delays or complications.
- Compromised communication systems, hindering communication between healthcare professionals and impacting patient care.
The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, which targeted healthcare organizations globally, demonstrated the devastating impact of zero-day vulnerabilities. The attack encrypted patient data, disrupting hospital operations and causing significant financial losses.
Impact on Finance
The financial sector is highly vulnerable to zero-day vulnerabilities due to its reliance on sophisticated IT systems for transactions, data storage, and online banking services. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to:
- Financial fraud and theft, with attackers gaining access to customer accounts and funds.
- Disruption of trading platforms and financial markets, potentially causing market instability and economic losses.
- Data breaches exposing sensitive customer information, including credit card details, account numbers, and financial transactions.
The 2014 Target data breach, which compromised millions of credit card details, highlights the severe consequences of zero-day vulnerabilities in the financial sector.
Impact on Government
Government agencies are prime targets for zero-day attacks due to their access to sensitive information, critical infrastructure, and national security secrets. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to:
- Espionage and data theft, compromising classified information and national security.
- Disruption of government services, including online voting, tax filing, and public safety systems.
- Cyberwarfare and sabotage, impacting critical infrastructure, such as power grids, communication networks, and transportation systems.
The 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack, which targeted government agencies and businesses worldwide, disrupted critical infrastructure and caused billions of dollars in damage.
Impact on Critical Infrastructure
Zero-day vulnerabilities can have devastating consequences for critical infrastructure, including power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to:
- Power outages, disrupting essential services and causing widespread economic damage.
- Disruption of transportation systems, including air traffic control, railways, and road networks, impacting travel and logistics.
- Communication disruptions, hindering communication and access to vital information.
The 2010 Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iran’s nuclear program, demonstrated the potential of zero-day vulnerabilities to cause significant damage to critical infrastructure.
Challenges and Opportunities in Protecting Against Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Protecting critical sectors from zero-day vulnerabilities presents significant challenges, requiring a multi-layered approach:
- Proactive vulnerability management: Regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities and patching them promptly.
- Threat intelligence: Monitoring for emerging threats and understanding attack trends.
- Security awareness training: Educating employees on best practices for cybersecurity and recognizing phishing attempts.
- Incident response planning: Developing plans for responding to security incidents and mitigating damage.
- Collaboration and information sharing: Sharing information about vulnerabilities and attacks with other organizations and government agencies.
The emergence of zero-day vulnerabilities highlights the importance of continuous innovation in cybersecurity. Organizations need to invest in advanced security solutions, such as intrusion detection systems, sandboxing, and threat intelligence platforms, to stay ahead of attackers.
Future Trends in Zero-Day Vulnerability Management
The landscape of zero-day vulnerabilities is constantly evolving, presenting ongoing challenges for security professionals. As attackers become more sophisticated and exploit new vulnerabilities, staying ahead of the curve requires a proactive approach. This section delves into emerging trends and strategies in zero-day vulnerability management.
The Importance of Collaboration and Information Sharing
Effective zero-day vulnerability management necessitates a collaborative approach involving industry stakeholders, security researchers, and government agencies. Sharing information about newly discovered vulnerabilities, threat intelligence, and best practices is crucial for collective defense. This collaborative approach allows for faster identification, mitigation, and response to zero-day exploits.
- Industry-Wide Collaboration: Sharing vulnerability data and best practices between technology companies, cybersecurity firms, and industry associations is vital. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape and facilitates the development of collective defense strategies.
- Security Researcher Collaboration: Encouraging responsible disclosure practices by security researchers and providing incentives for vulnerability reporting is essential. This allows for timely vulnerability patching and mitigation before attackers can exploit them.
- Government Agency Partnerships: Collaboration with government agencies, such as the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), is crucial for coordinating national security efforts and sharing intelligence about emerging threats.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI), have the potential to significantly impact the landscape of zero-day vulnerabilities. While these technologies offer numerous benefits, they also present new challenges for cybersecurity.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers have the potential to break current encryption algorithms, making it easier for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. This necessitates the development of new, quantum-resistant encryption methods to secure sensitive data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can be used by attackers to automate the discovery and exploitation of vulnerabilities. This requires the development of AI-powered security solutions to detect and prevent such attacks.
The battle against zero-day vulnerabilities is a constant struggle. While technology plays a vital role in identifying and mitigating these threats, human vigilance and proactive measures are equally crucial. Staying informed about emerging threats, implementing strong security practices, and fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders are essential steps in safeguarding our digital world. As technology evolves, so too will the challenges posed by zero-day vulnerabilities, requiring a continuous adaptation of security strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
FAQ Corner
How can I protect myself from zero-day vulnerabilities?
Staying up-to-date with the latest security patches, using strong passwords, and being cautious about suspicious links and attachments are crucial steps. Additionally, using reputable antivirus software and firewalls can help mitigate the risk.
What is the difference between a zero-day vulnerability and a known vulnerability?
A zero-day vulnerability is a flaw that is unknown to developers and for which no patches or defenses exist. A known vulnerability is a flaw that has been identified and for which a patch or workaround is available.
Are zero-day vulnerabilities a new threat?
Zero-day vulnerabilities have been around for a long time, but they have become increasingly prevalent in recent years due to the rapid pace of technological advancements and the growing sophistication of cyberattacks.
How can I report a zero-day vulnerability?
You can report a zero-day vulnerability to the vendor of the affected software or to a security research organization. Many organizations have responsible disclosure programs that allow you to report vulnerabilities in a safe and secure manner.






